Understanding the inner workings of a computer involves breaking down its various components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the system.
From the Central Processing Unit (CPU) that acts as the brain of the computer to the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) responsible for rendering images, every component has a specific function.
Lets delve into the key components of a computer, exploring their roles, features, and how they work together to create a fully functional computing device.
Introduction to a Computer and its Components
Welcome to the world of computer components, where we unravel the mysteries of the machines that power our digital lives.
Just like building blocks in a Lego set, each component plays a crucial role in the smooth operation of a computer.
Weather you are new to computers or just curious about how they work, we take a look at each part that makes up your general computer.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
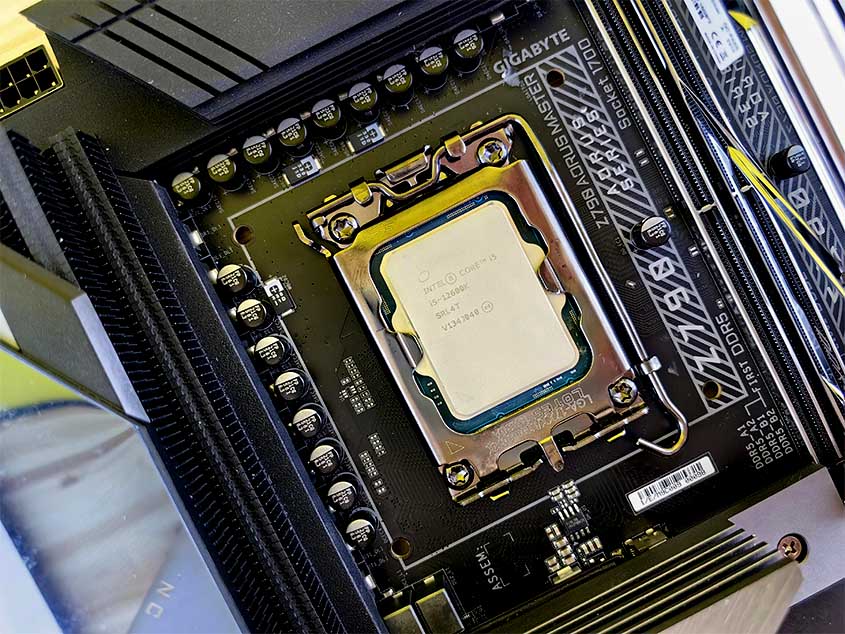

Function and Importance of the CPU Component
At the heart of every computer lies the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the brain behind all computing tasks.
Thus, a crucial part of a computer as this chip handles all the essential calculation and logic that makes up a computer.
CPU Architecture and Cores
Modern CPUs come with multiple cores, like a team of multitasking wizards tackling different tasks simultaneously. The architecture of a CPU determines its capabilities and performance, so choose wisely!
There are two top dogs in the PC industry today Intel and AMD (Advance Micro Devices). Both companies offer a wide range of CPU listings which each catering towards specific needs and goals. check out AMD vs Intel for Gaming in 2024? The Ultimate Breakdown if you want to know more about CPUs
CPU Clock Speed and Cache Memory
Clock speed measures how fast a CPU can process instructions, while cache memory acts like a handy assistant, storing frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
Together, they amp up your computer’s speed and responsiveness. Its common these days to have lots of CPU cores and less speeds, unless you look into the higher tier CPU listings.
Nowadays processors can reach speeds of 6 Ghz or higher.
Fun Fact: Did you know that AMD was the first company to break the 64bit architecture back in the early 2000’s?
That’s why in the Linux world you will often see amd64 being used for 64Bit Linux packages and intel i386 for 32Bit packages.
2. Random Access Memory (RAM)
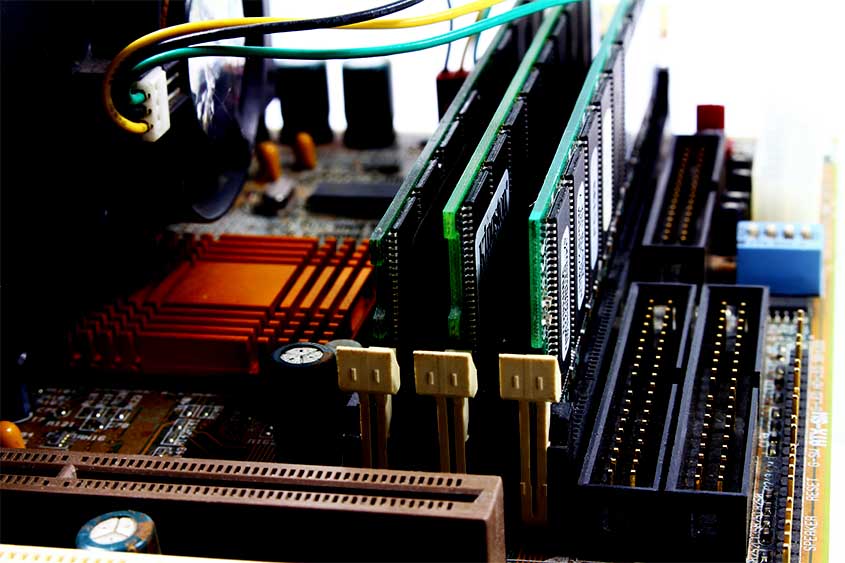

Role of RAM in Computer Operations
Random Access Memory or (RAM Memory) is like a temporary workspace where your computer stores data for quick access.
It is vastly faster than having the PC load data from the hard drive even if its an SSD type drive.
The more RAM you have, the more smoothly your computer can juggle multiple tasks without breaking a sweat.
These days is common for entry level computers to have 8 Gigabyte base memory and gaming or more performance driven PC’s to have 16 to 32 Gigabyte of memory.
Furthermore think of RAM memory as a mediator between the CPU and the Hard drive. Allowing the CPU to fetch data quicker by going to ram instead of your Hard Drive.
On computers that has Limited RAM installed the operating system such as Microsoft Windows or Linux Systems will use whats called a swap file or partition.
This acts like RAM but since its located on a hard drive you will see a significant drop in performance when the system starts to make use of that allocated memory when RAM runs low or out.
Types of RAM (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5)
RAM comes in different flavors, from DDR to DDR5, each offering varying speeds and capabilities.
Choosing the right type of RAM can supercharge your computer’s performance and efficiency. But take note that not all ram are the same.
The “DDR” or (Double Data Rate Memory) naming schema specifies which generation of RAM you need and depends on which type your motherboard supports.
RAM Capacity and Speed
When it comes to RAM, bigger isn’t always better. The speed of RAM as well as the CAS latency or RAM Timings play an important factor here as well.
The lower the CAS Latency the better the RAM will perform. Then there is also XMP profiles. These essentially act as a RAM overclock for your system and requires a compatible motherboard.
Intel overall are more forgiving when it comes to RAM speeds and Timings, If you plan in using AMD you need to be really careful when selecting compatible RAM.
The capacity and speed of your RAM determine how well your computer can handle demanding applications and multitasking.
Strike a balance to keep your system humming along happily. Many people over spec on RAM memory which can lead to a system that costs way more than what was needed for the task or roll it needs to fulfill.
Take for instance a Gaming system, it is really unnecessary to exceed 16 Gigabyte to have a good gaming expieriance in 2023 and 2024.
At most a system with 32 Gigabyte of DDR4 or DDR5 will be more than enough to handle pretty much all games out there.
Rather then spend on more RAM look at investing that into a Graphics Card instead of Gaming is your main goal.
However, if you need a production system such as software developers or content creators then a system with 32 Gigabyte of memory might be the bare minimum especially if you plan on running virtual environments.
3. Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs and NVME)
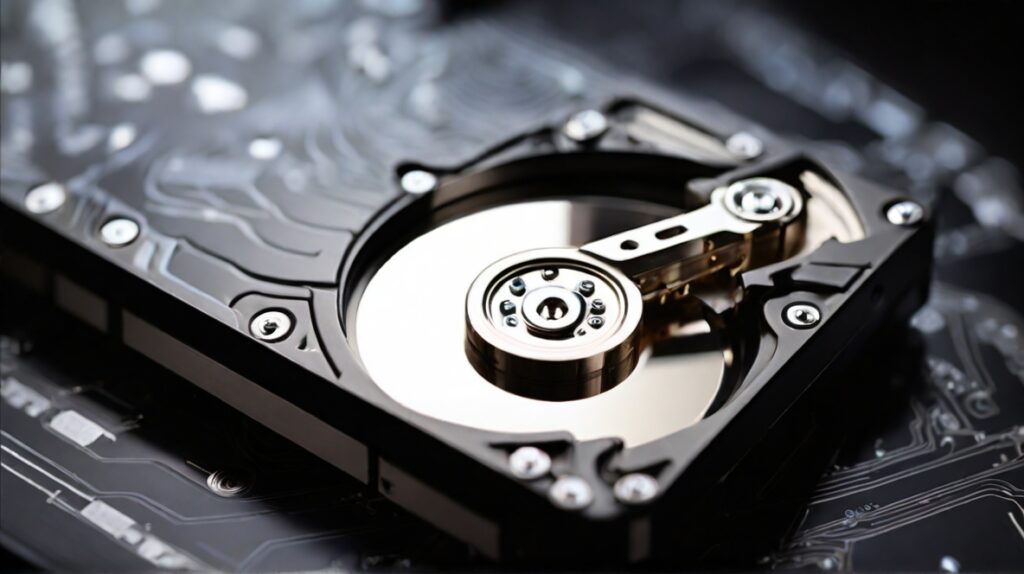

We all need a place to store our information right ? Else what would be the point of having a computer. This is where storage comes into play.
Hard Drive storage is different from RAM as it keeps your files after you power off your machine. where RAM will typically loose anything stored in it as soon as the power is off.
Nowadays you have a few different options when it comes to Hard Drive storage. Some faster than others. Lets take a look:
Traditional Spinning Hard Disk Drive (HDD):
The traditional workhorse. Uses spinning platters for storage, offering large capacities at a lower cost. However, they’re slower and more prone to physical damage.
Solid-State Drive (SSD):
Faster than HDDs, thanks to flash memory chips. no moving parts and they boot up and load programs quicker, but tend to be pricier for similar capacities.
NVMe SSD:
The latest and fastest SSD option. Uses a newer interface for even quicker data transfer speeds. Ideal for performance-critical tasks but comes with the highest price tag.
Just like SSD Hard Drives NVME SSD’s do not have moving parts and as a result uses less power as well.
If you are interested in a more in-dept look check out our article about How to install a new Hard Drive
Differences Between HDDs and SSDs
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs) are like the tortoise and the hare of storage devices.
Traditional Spinning Hard Drives offer spacious storage at a lower cost, while SSDs race ahead with blazing speed and durability using way less power so they are ideal for Laptops as well.
4. Role of the Motherboard in a Computer
The motherboard is where is all comes together – it connects all the components together and ensures they play nice. From your CPU to your storage devices, everything talks to each other through the motherboard.
Expansion slots on a motherboard allow you to add additional fucntonality to your system… PCI and PCIe slots are the most common types you’ll see.
Just pop in a graphics card, sound card, or maybe even a fancy new SSD, and watch your computer evolve into something even more awesome.
Furthermore its important to note that your motherboard will dictate which platform you are on, Intel or AMD most commonly, these CPU sockets are different for each manufacturer and platform with different generations also being altered.
In other words you cant install a CPU form 5 years ago into a new motherboard or install an AMD CPU onto an Intel type motherboard. It will simply not work.
Likewise there are also the case of chipsets. motherboard typically come in 3 or more chipset varieties per generation. Entry, standard and high end.
Both AMD and Intel have multiple options in this area and it can get confusing really quick. Its like the car industry and their models and engine sizes only much more confusing at times.
Motherboards comes in different sizes known as form factors. Take note of this as your PC case or tower you have will be the deciding factor on which motherboard you can install.
5. The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) or Graphics Card
Ah the GPU or Graphics card. It’s the secret sauce behind smooth gaming, crisp videos, and all those fancy graphics you see on screen.
Without a good GPU, your computer would be like a painter without a brush – boring and uninspired.
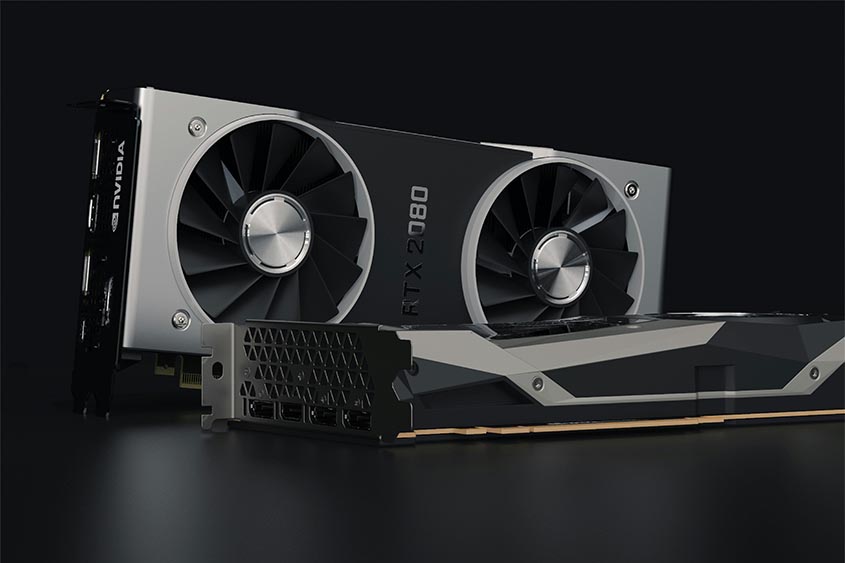

Types of GPUs (Integrated vs. Dedicated)
When it comes to GPUs, you have two flavors to choose from – integrated and dedicated.
Integrated Graphics are much less powerful and flexible and are often found on the CPU where your central processing Unit doubles as a light weight graphics processor as well. Both AMD and intel offer lineups that have or do not have integrated graphics.
Gamers and content creators usually opt for a dedicated graphics card instead of relaying on the integrated one and will therefore buy CPU’s that do not have them in to save on cost.
For most work stations and light computing tasks the integrated graphics processor or APU will be good enough.
Recently AMD has had good upwards success in shipping more powerful integrated graphics that is very capable. But again, depending on your needs these APU’s might not cut it.
The Big 3, NVIDIA, AMD Radeon and Intel
There are currently 2 major players in the Graphics race with a 3rd one coming in hot.
NVIDIA, is currently the leader in the graphics delivering excellent visuals and performance but at the premium price.
Generally the rule of thumb when it comes to picking a card is as follows:
- Nvidia 4050 or xx50 Series:
For basic 1080p medium to high graphics gaming and video work. - Nvidia 4060 or xx60 Series:
The 60 series is the mid range gaming card. used for 1080p and 1440p gaming on high settings. Most people opt for these. - Nvidia 4070 or xx70 Series:
Now we get to the higher tier, the 70 series from Nvidia usually caters for gaming and graphics workloads that require 2k or 4k gaming. costing more however. - Nvidia 4080 or xx80 Series:
For the enthusiast and people with lots of money to burn. these cards offer the pinnacle of performance but at a premium price tag. Its needed of 8k on ultra is your thing. Most of the time its unnecessary to opt for a card like this as you would also need to have a high tier CPU to keep up.
AMD Radeon range is not far behind offering a good alternative and in some cases better offers for the same if not lower price than NVIDIA.
Lastly there is Intel, with their ARC Battle Mage Series. While new to the graphics market its a very good attempt at giving users yet another option. But it needs some more time to mature and become one of the main stream options.
Years back AMD acquired the company ATi which was responsible for the Radeon Series, The alternative to NVIDIA and has since made huge strides in the Graphics card race.
6. Components Like The Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Importantly, the power supply and its quality is a very important factor in a computer system, most people overlook this key component.
Your Power Supply or PSU is the life blood of your machine. Skimping on a good brand or installing a low wattage power supply can lead to damage and issues.
Efficiency Ratings and PSU Safety
The PSU efficiency ratings are like the energy star ratings on appliances – the higher, the better. A more efficient PSU means less wasted power and lower electricity bills. Plus, a safe PSU is crucial for preventing electrical mishaps and keeping your computer running like a well-oiled machine.
Generally, its advised to avoid no name power supply brands. Look for a good 80 Plus bronze, Gold or even platinum rating and use a reputable manufacturer such as Corsair, Coolermaster, SeaSonic and Thermaltake to name a few.
Furthermore, the wattage of the Power Supply will need to cater for all your components. Use an online calculator if you are not sure.
Keep in mind that high end gaming systems can use up to over 1000w or more.
7. Cooling Systems and Fans
Good computer cooling is essential to keep the components in good working order and prolong the life expectancy of your PC overall.
Types of Cooling Systems (Air, Liquid)
Computers these days come with different thermal cooling solutions from active to passive cooling however there are two main ways computers and its components are kept cool.
Air Cooling: Simpler and more affordable, air cooling uses fans to circulate air. A heat sink, a metal finned structure (usually copper or aluminum), absorbs heat from components like the CPU or GPU. The fan blows air over the heat sink, carrying away the heat. This is sufficient for many computers, but can get loud under heavy use.
Liquid Cooling: More complex and expensive, liquid cooling uses a liquid coolant to absorb heat. A water block replaces the heat sink on the CPU. A pump circulates the coolant through a radiator with fans, similar to a car radiator. This pulls heat away from the components and out of the case, offering quieter operation and better cooling for high-performance systems.
Liquid cooling functions very much like a Car’s cooling system only on smaller scale.
You will often find that Liquid cooling is commonly found in Gaming systems, with ascetics and customization being key factors furthermore, when buying a CPU take note because some offerings from both Intel and AMD alike does not come with any cooling solution thus leaving you to make a plan and choose an option which can increase the cost of the system overall.
Fan Placement and Maintenance
Fan placement is crucial for optimal cooling – you don’t want hot air circulating around your computer like a sauna.
Proper airflow is key to keeping things cool and happy inside your system. And don’t forget to give your fans some love with regular maintenance – clean them up and make sure they’re spinning like champion windmills.
The general rule here is that front fans bring in cool air and top and rear fans exhaust hot air from the case. Optimally its a good idea to have more fans pulling in fresh cold air then extracting hot air.
This is also known as “Positive Pressure” inside the case and can aid on keeping dust out.
Negative Pressure leads to a computer collecting more dust as its struggled to find cool air and will act as a mini vacuum cleaner sucking air in from every nook and cranny, hole and space it can…
8. The component know was the PC Case
Lastly we look at the box or the enclosure that will accommodate all the other electronics. The Computers case is not only a personal preference but also needs to be though out when building a system.
Choosing a case will effect which components you can install, airflow and accessories. there are a few standard cases called:
Full Tower:
- Size: Largest case option (typically 55-75cm tall)
- Pros: Excellent airflow, space for multiple components and expansion cards, ideal for high-performance builds.
- Cons: Bulky and takes up a lot of desk space, can be expensive.
Mid Tower (ATX):
- Size: Most popular size (typically 35-48cm tall)
- Pros: Good balance of size, airflow, and expandability, suitable for most builds.
- Cons: Less space compared to full towers, might limit options for high-end components or multiple storage drives.
Mini Tower (mATX):
- Size: Compact option (typically 30-38cm tall)
- Pros: Small footprint, ideal for space-constrained environments, good for basic builds.
- Cons: Limited space for components and expansion cards, might not support high-performance hardware or bulky GPUs.
Small Form Factor (SFF):
- Size: Very compact (variable, often cube-shaped)
- Pros: Highly portable, perfect for HTPCs (home theater PCs) or minimal desk setups.
- Cons: Extremely limited space for components and cooling, restricted upgradeability.
Water Cooling Case:
- Size: Varies, often similar to mid-tower
- Pros: Designed specifically for liquid cooling systems, with radiator mounting points and optimized airflow for coolant flow.
- Cons: Generally more expensive than standard cases, might require additional research for compatible components.
Conclusion
By dissecting and understanding the components that make up a computer system, we gain insight into the intricacies of modern technology.
From the processing power of the CPU to the storage capabilities of HDDs and SSDs, each component contributes to the seamless operation of a computer.
As technology continues to evolve, grasping the fundamentals of computer components becomes increasingly important for users looking to optimize performance and stay informed in a rapidly advancing digital landscape.